Chemical Peel: What Are The Acids Used?
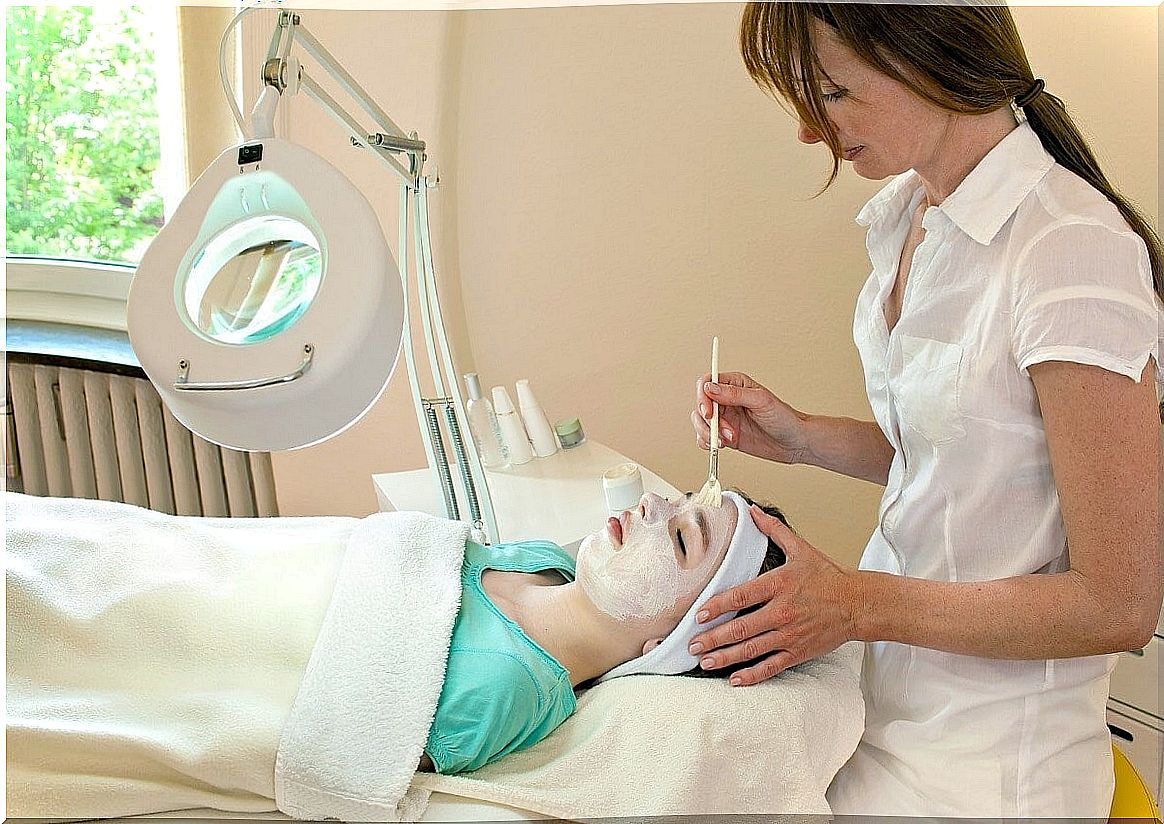
The peeling chemical also known as dermabrasion. In recent years it has managed to position itself as one of the most widely used aesthetic procedures, since its application helps to correct various skin imperfections.
In particular, it consists of the removal of a variable thickness of the epidermis or dermis through the use of chemical substances that are generally acidic or caustic. With this, it is possible to renew the superficial layers of the skin to minimize the presence of spots, wrinkles, among others. You wonder, what are the most used acids in this treatment?
What are the most used acids in chemical peels ?
When performing a chemical peel, it is convenient to know that there are several types of acids to carry out the procedure. The choice between one or the other varies according to the needs of the skin. Therefore, before applying it, the ideal is to have the advice of a professional dermatologist. Let’s see in detail the most used substances.
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAAs)
Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAAs) comprise a large family of compounds derived from fruits and natural substances. Due to their low toxicity, they produce almost no adverse effects and are easy to use.
In the meantime, once the treatment is done, the person can resume their daily activities without problems. For this reason, it is one of the most used chemical peels both in offices and in home formulations.
These acids have the advantage that they can be applied to almost all skin types, regardless of age. They even adapt to all phototypes. The best known in this category include the following:
- Malic
- Tartaric
- Citric
- Lactic
- Glycolic
- Kojic
- Ascorbic
- Mandelic
Because they belong to the same chemical “family,” they all share some properties, as well as having distinctive individual characteristics.

Properties of alpha hydroxy acids
Some are used to perform chemical peeling while others, which have less acid power, are used as depigmenting agents or complements to other treatments. Specifically, they stand out for the following benefits:
- Moisturizing (hydro-retaining) power: they produce a softening effect and increase skin comfort.
- Ability to regulate keratinization: they generate a moderate exfoliation and a renewing and “compacting” effect on the superficial layers of the skin.
- Anti- aging effect : a publication in the Synthetic Chemistry and Natural Product Chemistry magazine states that they attenuate small superficial wrinkles, reinforce the acidity of the superficial epidermal layers (which gives it greater defense against microbes), improve micro-relief and provide skin splendor.
Glycolic Acid
According to studies published in Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology , it is the best known and most used for its effectiveness and few adverse effects. Of all the acids, it is the one with the smallest molecule, so its penetration capacity is greater than other varieties.
They can have as good penetration as any other chemical peel , but scab, necrosis and scaling can be controlled and minimized if used in optimal conditions. Its main uses are the following:
- Photo damage in general.
- Actinic keratosis
- Solar lentiginosis.
- Acne and its sequelae.
- Post-inflammatory pigmentation.
- Melasma
- Xerosis
- Ichthyosis.
- Follicular keratosis.
Glycolic acid for medical use ranges from 30% to 70% in solution, gel or mask, according to the latest updates in Atdermae magazine .
You may be interested: Cosmetic routine: everything you need to know
Mandelic acid
It is a derivative of bitter almond extract. A publication in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology determined that it is the most used alpha hydroxy acid for hyperpigmentation and acne treatments due to its effectiveness.
Due to its origin from almonds, it has antimicrobial and antiseptic potential, and is even used as an oral medicine. It is indicated above all in people with melasma and acne spots. In addition, it is suitable for skin with rosacea or sensitivity.
The normal effects during the application of alpha hydroxy acids are burning sensation, tearing, redness and whitening of the skin. It is used at 30 or 50% in the office and up to 12% in home formulas.
Beta hydroxy acids (BHA)
The beta hydroxy acids (BHA) are a small group, of which salicylic acid is commonly used in dermatology and aesthetics. In aesthetic medicine, 10 to 30% is used in the office.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid has been used for many years for its keratolytic properties for topical use in the treatment of hyperkeratosis and peeling skin problems, such as dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, ichthyosis, psoriasis and acne.
Very recently it was published in Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology that it can be used safely in high phototypes. To be more exact, it can be applied for the following:
- Superficial acne scars.
- Active acne.
- Hyperkeratosis
- Dyschromias in general.
- Photoaging.
- Fine wrinkles
Read also: What is salicylic acid?
Skin care after chemical peel
After each chemical peel , the skin may feel tight, tender, dry, and pink to red. The fact of eliminating one or more layers of skin cells forces the body to start several processes that tend to regenerate the lost skin.
Emphasis should be placed on avoiding contact with the sun and the use of sunscreen. The use of petroleum jelly in a thin layer, or moisturizing creams, favors a slight flaking and without a feeling of tightness.
Despite its popularity, the peeling are not harmless, may alter the color and texture of the skin and leave scarring sequelae. According to medical criteria, they can be performed at any age, but it is not recommended for pregnant and lactating women.