Complementary Dengue Treatment: Natural Remedies
It is estimated that there are around 390 million cases of dengue per year, of which 96 are clinically manifested, regardless of severity. Although it is mainly treated with drugs, there is a set of measures that make up the complementary treatment of dengue and that help to relieve the patient.
A complementary treatment for dengue
Paracetamol is usually indicated in the treatment of dengue, but NSAIDs (including aspirin) should be avoided due to the risk of bleeding. On the other hand, the MSD Manual indicates that “aspirin increases the risk of Reye’s syndrome in children and should be avoided for that reason.”
In the popular sphere, different natural remedies have been used (in a complementary way) to provide the patient with the best possible relief when they have a fever. These remedies constitute the complementary treatment of dengue.
Most of the remedies are made up of plants that have compounds with antipyretic properties. It should be noted that, being mostly infusions, these remedies help the patient to stay hydrated and, in turn, replenish the minerals that may have been lost. Therefore, they become allies in case of dehydration.
But, although these remedies can alleviate some symptoms, it is very important to note that drugs prescribed by the doctor should never be excluded. These plants are a complement.
1. Carica papaya leaf
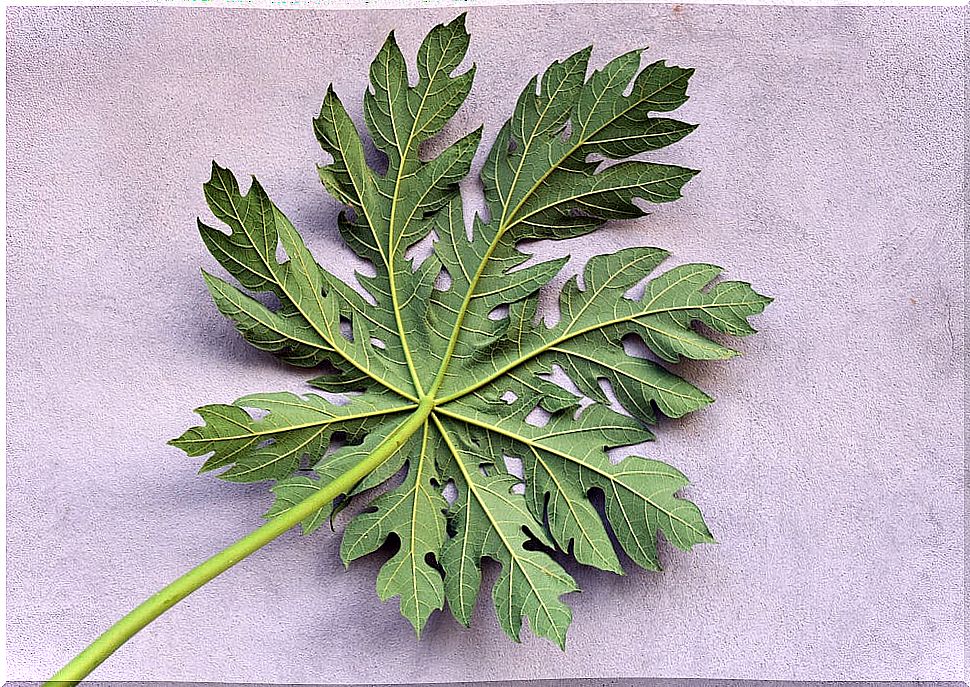

Its consumption produces an increase in the platelet count. This is because it contains flavonoids and phenols with high antioxidant power.
2. Euphorbia hirta (cauliflower or swallow grass)
This plant produces a moderate increase in the platelet count, as well as a significant increase in white blood cells (which improves leukopenia). It is used to alleviate the symptoms of a mosquito bite by placing (roasted) leaves on the skin.
3. Azadirachta indica (nim or Indian lilac)
As a complementary treatment for dengue, it is a powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory. It can be used as a natural repellent for mosquitoes.
4. Andrographis paniculata (androgra or kiryat)
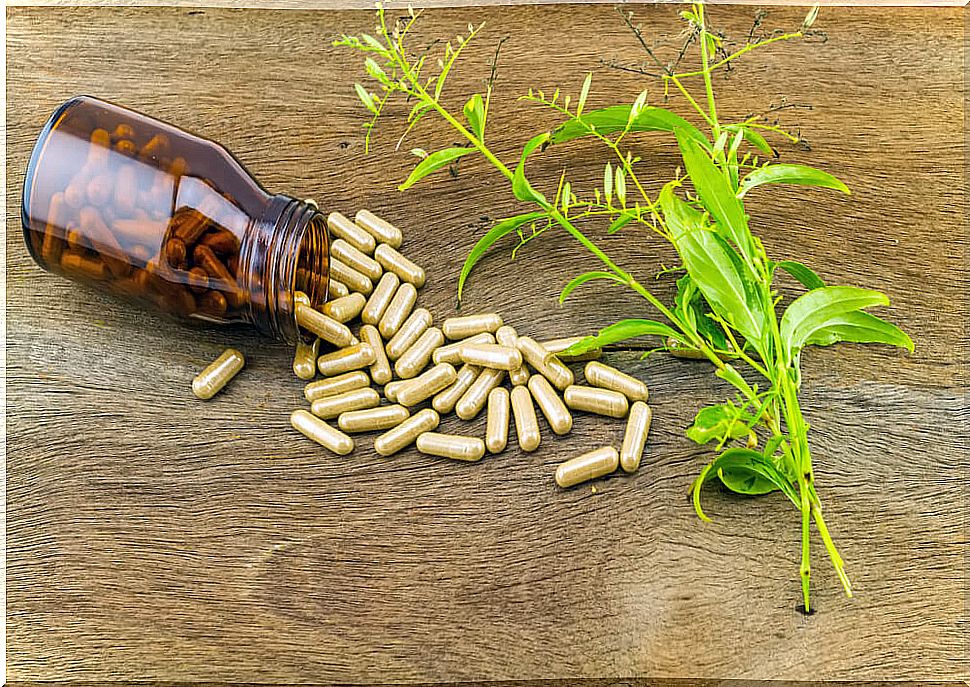

This plant has anti-inflammatory properties. The leaf extract is toxic against the Aedes aegypti vector , and at certain concentrations it can be used as a larvicide (this is still under study). It can be found in powder, tablets or capsules.
5. Tulsi or holy basil
The layer of perspiration that produces when lowering the fever is saline, which serves as a mosquito repellent. It is recommended to drink half a cup of this infusion every 2 hours to hydrate the body.
6. Barley grass
Since it contains chlorophyll, this herb stimulates the production of blood cells and therefore platelets. It is also rich in vitamins (C, B complex), minerals (magnesium, zinc, potassium, and sodium), and antioxidants.
You only need to boil the herb in a liter of water and drink the infusion throughout the day. But it can cause nausea or vomiting, so it is recommended to use its commercial powder presentation.
7. Fenugreek or fenugreek
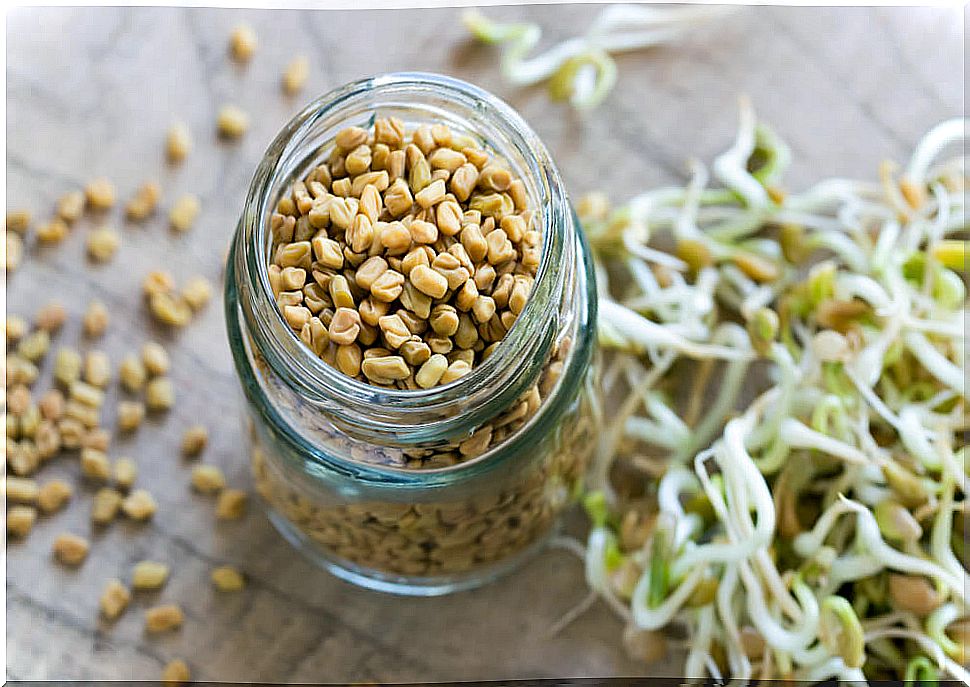

It helps to combat general discomfort, so it can also be used in case of flu. This plant has sedative properties that promote restful sleep and rest for the patient. It is recommended to eat some fenugreek leaves, previously washed, before each meal.
8. Basil leaf
It has antibacterial, antioxidant and antibiotic properties. This plant is very useful to treat all kinds of infections.
Basil oil has natural insecticidal properties and can be used as a repellent.
9. Hydrastis candensis (hydrastis or goldenseal )
It has minerals (magnesium, iron, and calcium) and vitamins (A, C, D, E, and B complex). It contains berberine, an alkaloid that has antibacterial, antifungal, and antiprotozoal properties.
recommendations
Before using any complementary dengue treatment, we recommend that you consult with your doctor about the possible interactions that you may have with the medications you take regularly and how you should proceed in this regard.
Caution is necessary in the case of pregnant or lactating women. Also in children under 2 years of age, patients with HIV or AIDS and patients with kidney (HTN), liver, gallbladder, cardiac, gastrointestinal (ulcers, GERD), hematological and ophthalmological pathologies.