Pitaya, The Pink Exotic Fruit
Pitaya is the fruit of the Hylocerus cacteus cactus . Coming from southern Mexico and Central America, there are different varieties of this tropical fruit. Among them is the one with pink skin that may have the pulp of the same color or white with small black seeds inside.
Despite having an exotic appearance, it has a flavor similar to that of many other fruits. Some people describe it with a taste between kiwi and pear. Both for those who hear about it for the first time and for those who have it among their fruits of regular consumption, in the following article we learn more about its composition and characteristics.
Pitaya properties and health benefits
Dragon fruit has aroused the interest of science in recent years due to its significant presence of nutrients. In this way, some of its most important effects have been known both for the food level and even for the cosmetics industry. Among its main benefits are the following.
Antioxidant
This is one of the main positive impacts of pitaya. As noted for a long time, it contains different compounds with this activity. Antioxidants are molecules that protect the cells of the body from the action of free radicals.
There is sufficient scientific evidence linking the latter to some chronic diseases such as arthritis, cancer, diabetes or heart disease. Although free radicals are not the only cause, a diet rich in antioxidants can be preventive.

Oligosaccharides with prebiotic effect
Part of the nutritional content of pitayas is made up of carbohydrates. Apart from glucose and fructose, it has notable amounts of oligosaccharides. These are more or less long sugar chains.
It has been observed that this type of fiber cannot be degraded by gastric juices and enzymes. In this way, it reaches the colon undigested where it serves as food for intestinal bacteria. This is why it can be said that the consumption of pitaya is capable of stimulating the growth of some strains, such as bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus .
The relationship between a healthy microbiota and good health has a lot to advance. Today it is known to exert an influence in some situations, such as inflammatory bowel diseases, irritable bowel syndrome, obesity, metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver.
Strengthens the immune system
The body’s ability to cope with pathogens depends on some dietary factors. In this way, cells, including those of the defense apparatus, have all the necessary nutrients to function optimally.
As experts point out, the role of vitamin C and zinc, both present in the pitaya fruit, stands out. Also from vitamin A (in this case beta-carotene, one of its precursors).
This nutrient has the ability to prevent infections, while ascorbic acid supports different cellular functions of the innate and acquired immune systems. In addition, a good part of these cells are found in the lymphoid tissue associated with the intestine.
The intestinal microbiota interacts with these, so all foods with a prebiotic effect keep it in good condition and facilitate this positive effect on the defenses.
Increase iron intake
Dragon fruit is one of the few fresh fruits that provides a considerable amount of iron. As will be seen later, in its nutritional composition, 1.9 mg per 100 grams of food represent around 10% of the necessary daily values of this mineral. The existence of vitamin C facilitates its absorption.
Make presence of fruits in the diet
It is significant to highlight the value of pitaya as part of the fruit food group. Most of them have positive nutritional characteristics. Including them in the daily diet has, in general, positive effects for health and well-being.
Eating 3 to 5 servings of fruits and vegetables a day is associated with a lower incidence of obesity, some types of cancer, and risk factors associated with cardiovascular problems, such as blood pressure. It also improves the state of the intestinal microbiota.
Nutritional composition
All the health properties of pitaya are due to some of its components. Its nutritional value is similar to that of most fruits with a high content of water, fiber and vitamins. The detailed composition per 100 grams of fruit is as follows:
- Water: 87 grams.
- Protein: 1.1 grams.
- Fat: 0.4 grams.
- Carbohydrates: 11 grams.
- Fiber: 3 grams.
In addition, in its composition some vitamins of group B stand out, such as B1, B2 and B3. It also has a remarkable amount of vitamin C and minerals such as calcium, iron, phosphorus and zinc. Finally, it is worth highlighting the presence of phytonutrients such as lycopenes (in the red flesh varieties), carotenes and phenols.
How to choose and eat pitaya
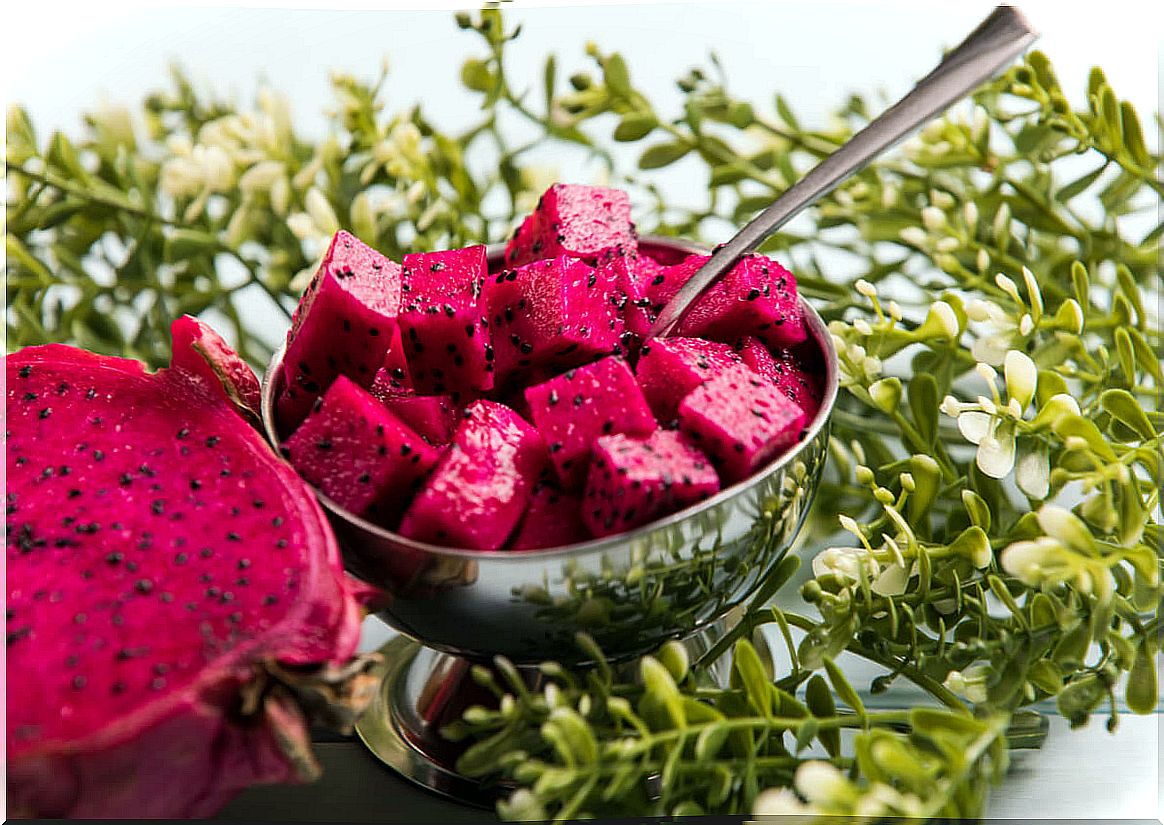

When selecting pitayas, they have to be bright red. Otherwise, if they are green, they are not just ripe. It is normal to have some spots on the skin, but if there are many, it is a sign that it is already very mature.
With a sharp knife it is cut in half lengthwise. The pulp can be separated with a spoon, just like when preparing an avocado. It is important to ensure that there is no piece of skin left, as it is not edible. Once peeled and cut they exist different ways of tasting it. We can do the following:
- Cut it into cubes and eat it alone or with other fruits.
- Incorporate it as one more ingredient in salads.
- Drink it in juices or smoothies along with other fruits. Yogurt or milk can be added to them.
Pitaya is an exotic fruit with great nutritional interest
The importance of introducing fruits into the daily diet is supported by its many benefits in the body. One of them may be the pitaya; without a doubt, one of the most striking on the market.
It is light, provides fiber and a large number of vitamins and minerals. Its presence is positive for preventing chronic diseases, improving the state of the intestinal microbiota and strengthening the immune system.